Telefónica’s Climate Action Plan: Driving Digitalization and Sustainability
Start Reading

1. Company at a Glance
In this case study, we will explore how Telefónica—a global giant in digital and telecommunications services—designed and implemented a Climate Action Plan that aligns sustainability with technological innovation. Through this initiative, Telefónica demonstrates how a company can decouple business growth from environmental impact, using digitalization not only to improve its own efficiency but also to help customers and suppliers reduce their emissions. By setting science-based targets, integrating climate goals into governance structures, and leveraging smart technologies to scale impact, Telefónica positions itself as both a responsible actor and a strategic enabler in the global transition to a low-carbon economy.
Telecommunications service provider
Industry
More than 100,000
Number of Employees
Madrid, Spain
Headquarters
Europe and Latin America
Global Presence

2. The Challenge
Telefónica launched its Climate Action Plan in 2022 in response to the urgent need to decouple business growth from environmental impact. As a global digital and telecommunications giant, the company recognized both its responsibility and opportunity to advance the sector toward a low-carbon future.
The decision to implement this practice was driven by multiple converging factors: increasing stakeholder expectations, stricter climate regulations, growing investor scrutiny and the recognition that digitalization can be a powerful enabler of decarbonization—both internally and for customers.
Telefónica saw sustainability not just as a risk to manage, but as a value driver and a core element of its long-term business strategy. Telefónica aligned its climate ambition with the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi), committing to reduce absolute emissions across its entire value chain.
The company set two key goals:
- Achieve net-zero emissions by 2040 across Scope 1, 2 and 3.
- Reduce 90% of its operational emissions (Scope 1 and 2) by 2025 in key markets including Spain, Brazil and Germany and offsetting these emissions of main markets annually as of 2025. This phased approach allowed Telefónica to focus first on high-impact markets
3. The Action
Telefónica’s Climate Action Plan is built around six interdependent models that address different dimensions of the company’s sustainability journey. These models translate high-level climate commitments into practical, measurable actions across operations, resilience, supply chain, products, financing, and governance
Operational Model: Decoupling Growth from Emissions
This model focuses on reducing Scope 1 and 2 emissions by transforming internal operations with the implementation adapted to the regulations and specific characteristics of each country:
- Energy Efficiency Plan: Telefónica has implemented large-scale efficiency measures, including the modernization of network equipment, introduction of Power Saving Features (PSFs), and infrastructure upgrades. These actions have enabled a reduction of 8% in energy use, despite a 9.3x increase in network traffic since 2015.
- Renewable Energy Plan: The company expanded its use of renewable electricity through Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs), self-generation projects and renewable energy certificates. Their plan is a global one, adapted to the needs and regulation of each market. By 2024, 89% of electricity consumption was renewable, with the goal of reaching 100% globally by 2030.
- Emissions Reduction Initiatives: Telefónica replaced fossil fuels with cleaner alternatives, installed hybrid self-generation systems, and adopted lithium batteries to reduce emissions from stationary sources and its vehicle fleet.
Adaptation Model: Increasing the Climate Resilience of the Company
Telefónica aims to increase the resilience of the company’s infrastructure to climaterelated effects, based on:
- Business Continuity: Telefónica has a global crisis and business continuity system, along with an insurance programme designed to prevent, respond to and mitigate service disruption in the event of extreme weather events, such as floods, landslides, droughts or storms.
- Preventive strategy through renewable energy and energy efficiency: Aiming at making the company less vulnerable to climaterelated risks, energy efficiency reduces consumption and improves the resilience of infrastructures and renewable energies increase energy self-sufficiency and reduce exposure to price volatility
Value Chain Model: Reducing Scope 3 Through Collaboration
Telefónica targets the most carbon-intensive part of its footprint—its supply chain:
- Supplier engagement: Through its Supplier Engagement Programme, Telefónica works with key suppliers (accounting for roughly 90% of its supply chain emissions) to improve their climate strategy and actions. Suppliers are classified into different maturity levels on the basis of CDP data, given tailored capacity-building and asked to commit to pledges (e.g. to set science-based targets) to move up to a higher maturity level next year. The programme efficiency is measured by supplier maturity improvement over years. Sector collaboration is key to amplifying the impact of these actions. Telefónica is part of the Joint Alliance for CSR (JAC) sector initiative, where 31 telecom operators share efforts to drive climate action in the supply chain as a sector.
- Circular economy integration: Initiatives like the MAIA marketplace and APOLO/VICKY programs promote the reuse, refurbishment, and recycling of network equipment and materials—cutting down on virgin resource use and Scope 3 emissions.
Commercial Model: Enabling Customer Decarbonization
Telefónica positions its digital services as tools for climate impact:
- Eco Smart Solutions: The company offers B2B digital tools (Internet of Things, cloud, big data) that improve energy efficiency, water management, and emissions reduction. The Eco Smart seal identifies the environmental benefit of each solution.
- Sustainable Consumer Engagement: Initiatives such as Eco Rating for mobile devices and the sale of refurbished phones help guide customers toward more sustainable purchasing decisions and extend product life cycles. Beyond informing consumers about the environmental performance of mobile phones, Eco Rating also encourages manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. By providing comparative information across brands and models, it increases competitive pressure on manufacturers to improve handset design, thereby reducing environmental impact, fostering industry-wide alignment, and enhancing transparency
Economic Model: Financing the Green Transition
Telefónica ensures environmental and financial sustainability go hand in hand:
- Sustainable finance instruments: The company leverages green bonds and sustainability-linked loans to fund climate-positive projects. By the end of 2024, the company achieved 37.4% financing linked to sustainability criteria. Since 2019, these projects have prevented over 1 million tonnes of CO2 e emissions.
- Internal Carbon Pricing: Telefónica uses a shadow carbon price to guide procurement toward lower-carbon technologies. This internal carbon price is implemented in purchasing decisions for equipment with electricity and/ or fuel consumption, as well as equipment containing refrigerant gases. By calculating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) where the cost of GHG emissions is also incorporated, procurement processes are guided towards more efficient equipment which avoids future GHG emissions. It is also developing an internal carbon fee that could support its neutralisation strategy.
Governance and Advocacy Model: Driving Alignment and Accountability
This model integrates climate action into corporate governance and stakeholder engagement:
- Strategic Governance: Climate responsibilities are distributed across the Board of Directors, the Sustainability and Regulation Committee, and operational leadership teams, ensuring alignment and oversight.
- Employee involvement: Staff receive climate training, and part of their variable compensation is tied to ESG performance, reinforcing ownership and awareness across the company.
- Transparency and advocacy: Telefónica maintains transparent reporting aligned with international frameworks (e.g., CDP, SBTi) and actively participates in climate policy advocacy. This includes leadership roles in the European Telecommunications Network Operators’ Association (ETNO) and GSMA working groups, and engaging in EU consultations to promote the inclusion of telecom networks in sustainable finance regulations (i.e., the EU Taxonomy for Sustainable Activities).
4. Overcoming Barriers
Operational Challenges
Network transformation and legacy system shutdown
Modernizing infrastructure while phasing out older technologies posed technical and logistical challenges. Telefónica responded by launching the Sustainable Platform Design project in 2022, which promotes energy-efficient technology deployment, circular economy practices, and the systematic decommissioning of legacy systems.
Supply chain engagement for Scope 3 reductions
Achieving Scope 3 emission reductions required deep collaboration with suppliers—many of whom operate outside Telefónica’s direct control. Through its Supplier Engagement Programme, the Company supported suppliers in setting science-based targets and encouraged participation in initiatives like the CDP Supply Chain programme to accelerate their decarbonization efforts. Telefónica leads a sectoral working group in the JAC initiative, where 31 telecom operators share efforts to drive climate action in ICT sector supply chains.
Cultural Challenges
Employee engagement and internal alignment
Embedding climate goals across diverse teams required significant cultural transformation. Telefónica addressed this by offering ongoing sustainability training and linking part of employee variable remuneration to ESG-related performance, fostering a shared sense of ownership.
Meeting growing stakeholder expectations
With rising demands from investors, customers, and regulators, Telefónica faced pressure to prove credibility and transparency. The company reinforced stakeholder trust through robust reporting practices and proactive climate advocacy at national and industry levels.
Financial Challenges
Upfront investment in green technologies
Transitioning to energy-efficient infrastructure and renewable energy sources required significant capital investment. Telefónica addressed this by leveraging green bonds, sustainability-linked loans, and internal carbon pricing mechanisms to align financial and environmental goals—ensuring the climate strategy was economically viable in the long term.
5. Impact & Results
Emissions reduction
Telefónica achieved an 84.8% reduction in Scope 1 and 2 emissions by 2024 compared to 2015— preventing 1.54 million tonnes of CO₂e from reaching the atmosphere
Scope 3 emissions (value chain) were reduced by 31.3% compared to 2016, equivalent to 893 kt of CO₂e.
Energy efficiency
Despite an 9.3-fold increase in network traffic, overall energy consumption decreased by 8%
The company improved energy efficiency per traffic unit by 90% since 2015, which has led to savings of more than €540 million thanks to the implementation of energy efficiency and energy management projects.
Renewable energy
In 2024, 100% of electricity in key markets (Spain, Germany, Brazil) was renewable; globally, 89% of electricity consumption in own facilities was from renewable sources.
Long-term renewable energy agreements secure clean electricity supply for more than a decade.
Sustainable finance
Telefónica reached 37,4% financing linked to sustainability criteria by the end of 2024, supporting network efficiency and climate-related investments.
Circular economy and waste reduction
In 2024, the company reused 533,818 network equipment items (+70% vs. previous year) and collected 437,180 mobile devices for reuse.
Employee and stakeholder engagement
Employees received continuous training on climate and sustainability, with ESG objectives tied to variable compensation. The compensation is linked to the fulfilment of ESG targets by the company
Customers benefited from Eco Smart solutions, while the Eco Rating system and device refurbishment initiatives promoted sustainable consumption.
Telefónica supported suppliers in improving climate performance, i.a. via setting science-based targets,through the Supplier Engagement Programme, as explained above.
6. Key Lessons Learned
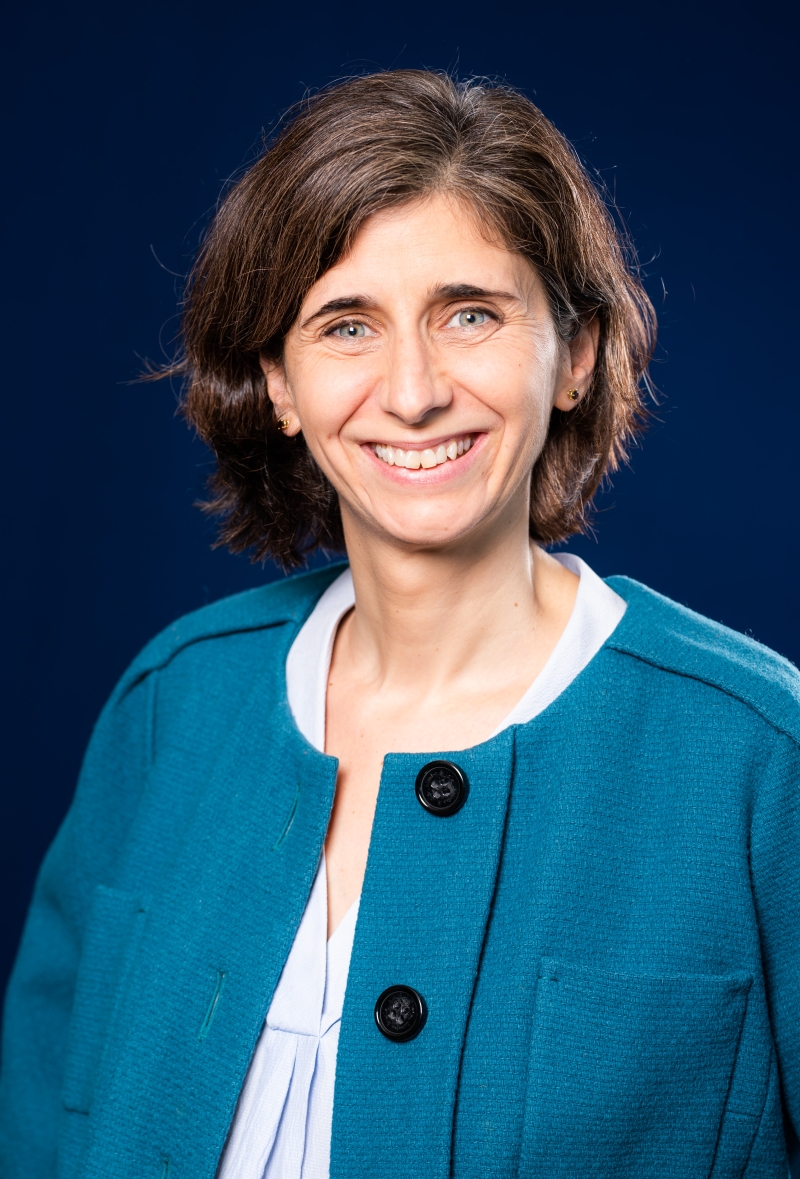


"We are working to accelerate responsible digitalisation that enhances competitiveness and generates a positive impact for all. In addition to reducing our emissions and increasing the resilience of our operations, we help other companies to become more efficient and lower their carbon footprint. Our networks and our digital solutions are powerful enablers of the green transition."
Maya Ormazabal, Global Chief Sustainability Officer at Telefónica
7. Company Commitment
Telefónica has been a committed participant of the UN Global Compact since 2012:
Forward Faster signatories in climate and living wage targets
Part of the SBTi initiative
8. Recommended Resources
Recommended UN Global Compact resources to support your journey:

E-Learning: Setting Science-Based Targets

E-Learning: The Net-Zero Standard

Climate Ambition Accelerator

Climate Action Plan 2025 Report
Download Case Study
Disclaimer: This case example is intended strictly for learning purposes and does not constitute an endorsement of the individual companies by the UN Global Compact.